Currently Empty: $0.00

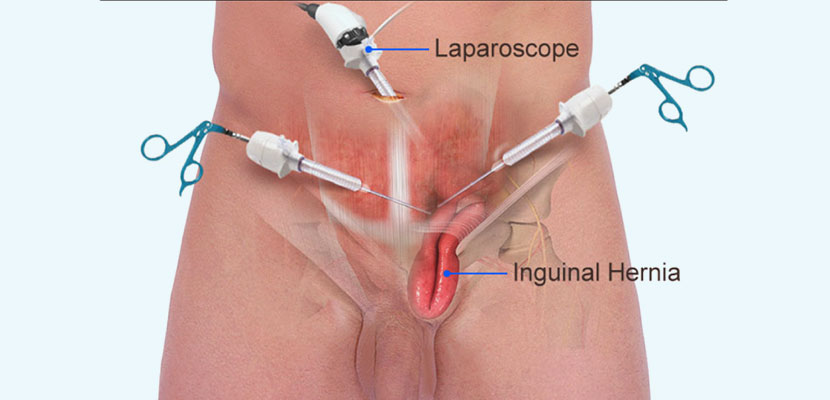
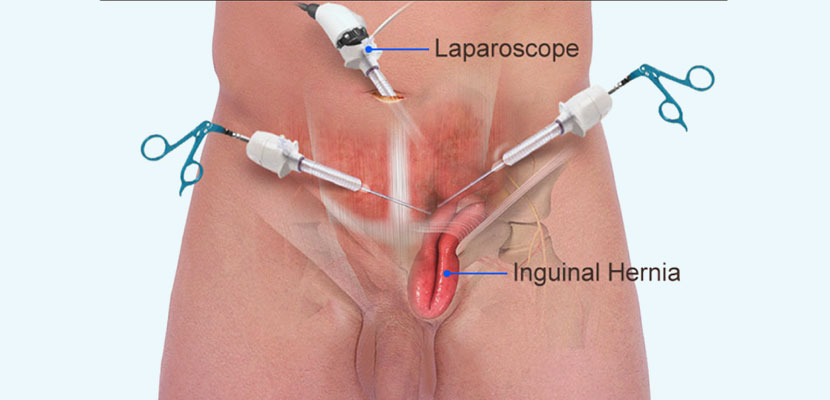
Open Inguinal Hernia Surgery in Hyderabad: Costs & Recovery
Introduction to Open Hernia Surgery
Definition of Incisional and Inguinal Hernias
A hernia occurs when an organ or tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. There are various types of hernias, with incisional and inguinal being among the most common in surgical contexts.
- Incisional Hernias: These develop at the site of a previous surgical incision. When the abdominal wall does not heal properly after surgery, a gap may form, allowing internal tissues or organs to push through.
- Open Inguinal Hernia Repair: Also known as herniorrhaphy or hernioplasty, it is a surgical procedure to fix groin hernias. This involves making a long incision in the groin area, with the hernia sac being either repositioned or removed. Traditionally, the repair was done by sewing healthy tissue, but now synthetic mesh patches are commonly used, particularly for large or recurring hernias.


Explanation of How Hernias Develop at Surgical Sites
Hernias often develop at surgical sites due to a failure in the healing process. When a surgical incision is made, and the layers of abdominal muscles are disrupted, the site becomes vulnerable. If the surgical site does not heal correctly or is placed under too much postoperative strain, it can weaken, creating an opportunity for internal tissues to push through. Factors such as infection, poor nutrition, and repetitive strain can exacerbate this weakness, leading to hernia formation.
Overview of When Surgical Intervention is Necessary
Surgical intervention is essential in many cases of hernias to prevent serious complications. Here are primary scenarios when surgery is recommended:
- Pain and Discomfort: Hernias that cause significant pain and impact daily activities typically require surgical repair.
- Symptoms: Symptoms such as swelling, a noticeable bulge, and discomfort warrant surgical evaluation.
- Complications: For hernias that are incarcerated (trapped) or strangulated (cutting off blood supply to trapped tissue), immediate surgery is crucial to prevent life-threatening complications.
- Children: Inguinal hernias in children are always recommended for surgical repair irrespective of symptoms due to the high risk of complications.
Understanding when surgical intervention is necessary helps in effectively managing hernias and avoiding potential complications. This preparation sets the foundation for exploring the different surgical techniques that can be employed in hernia repairs.
Surgical Techniques
Traditional Herniorrhaphy Technique Using Stitches
Herniorrhaphy is a traditional surgical method for repairing inguinal hernias, involving the manual stitching of tissue. In this technique, surgeons make a single long incision in the groin area. The hernia sac is either pushed back into the abdomen or removed entirely. The weakened muscle wall, where the hernia protrudes, is then stitched together using sutures. This method is particularly suitable for small hernias that have been present since birth, known as indirect hernias, and for cases where the muscle tissue is still robust enough to be sewn without causing undue tension and stress.
Modern Hernioplasty Approach Using Synthetic Mesh Patches
Modern hernia repair often involves the use of synthetic mesh patches, known as hernioplasty. This advanced technique is especially beneficial for large hernias and those prone to reoccurrence. After the long incision is made and the hernia sac is managed, a mesh patch of synthetic material is positioned over the weakened muscle area. This mesh reinforces the muscle wall and significantly reduces the recurrence rate by distributing the tension more evenly across the abdomen. The use of mesh patches in hernia repair has become a preferred method due to its effectiveness in reducing strain on the repair site and minimizing the likelihood of future hernia development.
Comparison of Different Repair Methods Based on Hernia Size and Type
When comparing traditional herniorrhaphy and modern hernioplasty, several factors come into play, including the size and type of the hernia, as well as the patient’s overall health and the surgeon’s experience.
Traditional Herniorrhaphy:
- Best suited for small, non-recurrent hernias.
- Preferable for patients with healthy surrounding muscle tissue.
- May involve higher tension on stitches, increasing the risk of recurrence.
Modern Hernioplasty:
- Recommended for large or recurrent hernias.
- Utilizes a synthetic mesh to reinforce the muscle wall.
- Offers a lower recurrence rate and distributes stress more effectively.
Both methods have their merits and are chosen based on the specific circumstances surrounding the hernia. In practice, hernioplasty is widely favoured due to its lower recurrence rates and reduced post-operative discomfort. However, it’s crucial for each case to be evaluated individually, considering the size of the hernia and the patient’s medical history.
Evaluating these techniques helps identify the most beneficial approach, ensuring the best outcomes for hernia repair.
Pre-operative Preparation
Required Diagnostic Tests and Evaluations
Before undergoing open inguinal hernia repair, several diagnostic tests and evaluations are necessary to ensure patient readiness and minimize surgical risks. Common preparatory tests include:
- Blood Tests: These assess general health, reveal conditions like anaemia, and provide essential clues about kidney and liver functionality.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG helps detect heart issues, imperative for assessing the patient’s fitness for anaesthesia and surgery.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound or CT scans of the hernia site provide detailed structural views, critical for the surgeon’s planning.
Conducting these evaluations is crucial as they help in formulating a comprehensive surgical plan and identifying potential complications.
Lifestyle Modifications
Smoking Cessation
Smoking is known to impede wound healing and increase the risk of post-operative complications such as infections. Therefore, patients are strongly advised to quit smoking at least a few weeks before surgery. Support to cease smoking may include nicotine replacement therapies or smoking cessation programs, which should be discussed with healthcare providers.
Weight Management
Excess body weight can exacerbate hernias and complicate both surgery and recovery. Effective weight management through a balanced diet and regular physical activity is recommended before surgery. Reducing weight not only eases the surgical procedure but also significantly enhances healing and reduces recurrence probability.
Preoperative Instructions and Restrictions
To ensure optimal surgical outcomes, patients must adhere to specific instructions and restrictions:
- Fasting Protocol: Patients are typically required to fast from midnight before the surgery day to avoid complications during anaesthesia.
- Medication Adjustments: Some medications, especially blood thinners, may need to be paused to reduce bleeding risks during surgery. Always consult with the surgeon or anaesthetist before making any changes to medication regimes.
- Hygiene: Patients should take a shower using antiseptic soap the night before and the morning of the surgery to reduce infection risks.
- Rest and Support: Arranging for post-operative support, whether from family or friends, ensures that patients can rest and recover without undue strain in the initial days following the surgery.
Patients must diligently follow these preoperative measures to ensure their bodies are adequately prepared for the surgical repair of their inguinal hernia. This level of preparation marks the foundation of a successful surgery and subsequent recovery.
Lastly, understanding and employing these practices allow for a smoother, more efficient surgical process and transition into post-surgical care and recovery.
Surgical Procedure
Step-by-Step Description of the Surgical Process
Open inguinal hernia repair involves a detailed surgical procedure aimed at repositioning the protruded abdominal contents and reinforcing the weakened muscle wall. The surgery usually starts with making a single long incision in the groin area. This exposes the hernial sac, which is then carefully pushed back into the abdominal cavity, or sometimes tied off and removed.
For smaller hernias and robust muscle tissue, traditional herniorrhaphy might be employed, wherein the edges of healthy muscle tissue are sewn together to close the defect. However, for larger or recurrent hernias, modern hernioplasty is preferred. In this approach, a synthetic mesh patch is placed over the weakened area to provide added support. The mesh is then secured with sutures, reducing tension on the muscle wall and lowering the risk of recurrence.
Types of Anesthesia Used
Anesthesia plays a crucial role in the comfort and safety of the patient during surgery. Open inguinal hernia repair can be performed under general anesthesia, where the patient is completely unconscious, or under regional anesthesia, such as spinal anesthesia, which numbs the lower part of the body while the patient remains awake. Local anesthesia combined with sedation may also be utilised, depending on the patient’s health condition and surgeon’s preference.
Typical Duration of Surgery
The duration of open inguinal hernia repair can vary depending on factors such as the size and complexity of the hernia, the patient’s overall health, and the surgeon’s experience. Typically, the surgery takes about 90 minutes to 3 hours to complete. The length of the procedure ensures thorough repair while minimizing risks of complications.
The patient preparation concludes, setting the stage for the recovery and rehabilitation phase, which is crucial for optimal post-operative outcomes.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Expected Hospital Stay Duration
Following open inguinal hernia repair surgery, most patients are typically required to stay in the hospital for around one to two days. This timeframe allows medical professionals to monitor for immediate postoperative complications such as infection or bleeding, ensure the proper management of pain, and verify that the patient can resume basic functions and tolerate oral intake before discharge.
Gradual Return to Daily Activities Timeline
The timeline for returning to daily activities after open inguinal hernia repair is vital to a successful recovery. Initially, patients are encouraged to begin light walking as soon as possible to promote circulation and reduce the risk of blood clots. Gradual increase in activity levels should follow these general guidelines:
- First Few Days: Light walking around the home is recommended.
- Within 2 Weeks: Most patients can return to light daily activities, such as desk work or household tasks that do not strain the surgery site.
- 3 to 6 Weeks: A more comprehensive return to normal activities is encouraged. However, lifting heavy objects and strenuous exercise should be avoided until the 6-week mark to ensure optimal healing.
Post-operative Care and Restrictions
Postoperative care focuses on wound care, pain management, and activity modifications:
- Wound Care: The surgical site must remain clean and dry. Patients should follow specific instructions provided by their surgeon regarding bathing and dressing changes.
- Pain Management: Prescribed pain medications should be taken as directed to manage discomfort. Over-the-counter pain relievers may also be recommended.
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in fibre is advised to prevent constipation, which can cause undue pressure on the surgical site during bowel movements.
- Activity Restrictions: Avoid lifting objects heavier than 10 pounds, strenuous activities, and any movements that induce pain at the surgery site.
Patients should keep an eye out for any signs of complications, including increased redness, swelling, severe pain, or fever, and contact their healthcare provider if any of these symptoms occur.
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial for monitoring the healing process and addressing any concerns early. The majority of patients return to normal activities without significant issues, but adherence to these guidelines is essential for a successful recovery.
With the right care and gradual reintroduction to daily activities, many patients achieve a full recovery, reducing the likelihood of hernia recurrence and enhancing overall outcomes.
Risks and Complications
Common Complications
While open inguinal hernia repair is generally safe, it carries some common risks inherent to surgical procedures. The most notable complications include infection and bleeding.
- Postoperative Infections: Infections can occur at the incision site and typically present with redness, swelling, warmth, and sometimes pus discharge. Fever may also accompany these symptoms. Proper wound care, antibiotics, and sometimes additional interventions are essential for managing infections effectively.
- Bleeding: Bleeding can happen during or after surgery. Mild bleeding usually resolves on its own or with minor interventions, but in some cases, more significant bleeding may require further surgical procedures to control.
Specific Risks
Apart from the general complications, specific risks associated with open inguinal hernia repair include potential nerve damage and testicular complications.
- Nerve Damage: Nerves running through the surgical area can be inadvertently harmed during the procedure. This may result in chronic pain or numbness around the groin or upper thigh. Nerve damage can sometimes be managed with medications or further surgical intervention if severe.
- Testicular Complications: In males, damage to the blood supply of the testicles or the spermatic cord during surgery can lead to testicular atrophy or issues with fertility. Careful surgical techniques and postoperative monitoring are crucial to minimise these risks.
Potential Long-Term Implications
Open inguinal hernia repair is usually successful, but certain long-term implications may arise that patients need to be aware of.
- Chronic Pain: Though rare, some patients might experience persistent pain post-surgery due to nerve entrapment or scar tissue formation.
- Recurrence of Hernia: Despite a successful repair, there is always a risk of the hernia recurring. Using synthetic mesh reduces this risk but does not eliminate it entirely.
- Scar Formation: While scars are a natural part of the healing process, extensive or keloid scarring can cause cosmetic concerns and sometimes impinge on surrounding tissues, causing discomfort.
Understanding these potential complications helps in recognising symptoms early and seeking timely medical intervention. Regular follow-ups with the healthcare provider ensure proper healing and reduce the chances of unwanted outcomes.
Next, evaluating the financial aspects of hernia repair surgery can provide a broader understanding of treatment planning.
Cost Considerations
Price Ranges for Different Surgical Techniques in Hyderabad
In Hyderabad, the cost of open inguinal hernia repair surgery varies depending on the technique used. Here are the typical price ranges:
- Traditional Herniorrhaphy: This technique, involving the use of stitches, generally costs between Rs. 42,000 and Rs. 71,000.
- Hernioplasty (Mesh Repair): This modern approach utilises synthetic mesh patches and ranges from Rs. 75,000 to Rs. 90,000.
- Laparoscopic Hernia Repair: This minimally invasive option tends to be more expensive, costing between Rs. 85,000 and Rs. 110,000.
These figures offer a broad estimate and actual expenses can vary based on the hospital, surgeon’s expertise, and specific patient needs .
Factors Affecting Overall Treatment Expenses
Several factors play a role in determining the overall expenses of hernia repair surgery:
- Type of Surgery: Open surgeries are generally less expensive than laparoscopic procedures due to the latter’s need for advanced equipment and technology.
- Hospital Fees: These include room charges, operation theatre costs, and nursing care.
- Surgeon’s Fees: Experienced and highly qualified surgeons may charge more.
- Pre-operative and Post-operative Care: Diagnostic tests, medical imaging, and follow-up consultations add to the costs.
- Anesthesia Fees: The type and duration of anesthesia used during surgery can also influence the overall price.
- Insurance Coverage: Comprehensive health insurance plans can significantly reduce out-of-pocket expenses for patients.
Understanding these cost components is crucial for patients to plan their finances and explore potential savings through insurance or other means.
Maintaining transparency and being aware of all potential costs can help in making informed decisions about hernia repair surgery, ensuring that patients receive the necessary care without unforeseen financial strain.
Take the first step toward hassle-free hernia treatment today! At Magicward, we make it simple to compare surgery costs and find the best hospital tailored to your needs. Fill out the form now to receive personalized quotations from top hospitals in Hyderabad. Your health is our priority—let Magicward guide you to the right care at the right price!

