Currently Empty: $0.00

Hysterectomy in Hyderabad: Expert Care for Women’s Health
Understanding Hysterectomy
Definition of Hysterectomy
A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the uterus. This operation is commonly performed to treat various medical conditions that affect a woman’s reproductive system. After undergoing a hysterectomy, the patient will no longer menstruate or be able to conceive a child.


Prevalence of the Procedure
Hysterectomies are quite common, Approximately 3 out of every 100 women aged 15 to 49 have undergone a hysterectomy, which is a surgical procedure involving the removal of the uterus in India . This statistic highlights the prevalence of hysterectomy as a treatment option for various gynecological issues within this age group, reflecting its role in addressing chronic conditions like fibroids and endometriosis that significantly impact women’s health and quality of life.
. This makes it one of the most frequently conducted surgeries among women, second only to cesarean sections. Women in the age group of 40 to 50 years are the most likely to undergo this procedure.
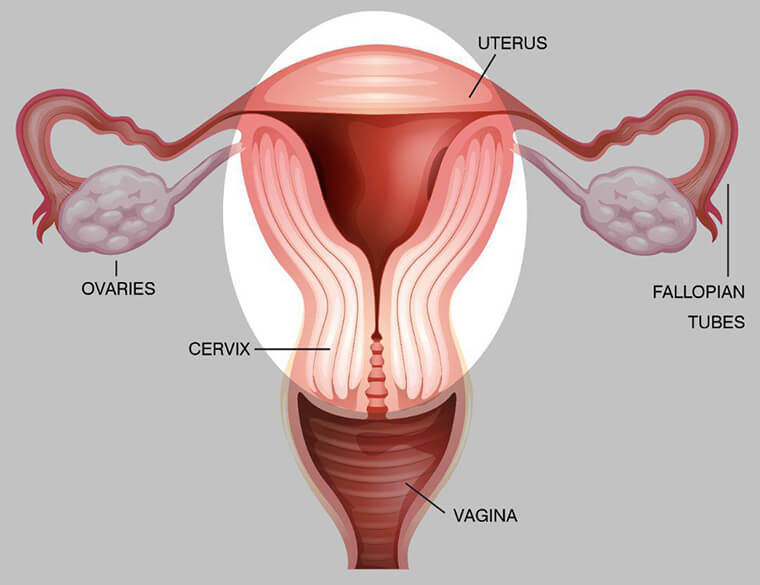
Basic Anatomical Considerations
The uterus, also known as the womb, is a key organ in the female reproductive system. It is located in the pelvis, positioned between the bladder and the rectum. The primary function of the uterus is to house and nourish a fetus during pregnancy. Besides the uterus, other reproductive organs, such as the cervix, ovaries, and fallopian tubes, are often considered during a hysterectomy. Depending on the specific medical need, these organs may also be removed during the procedure to ensure comprehensive treatment.
A comprehensive understanding of hysterectomy not only includes its definition and prevalence but also appreciates the anatomical considerations involved. This foundational knowledge sets the stage for exploring the various medical reasons for hysterectomy.
Medical Reasons for Hysterectomy
Common Conditions Necessitating a Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is often performed to treat several significant medical conditions. For instance, gynecological cancers, such as cervical, ovarian, and uterine cancers, frequently necessitate the surgical removal of the uterus. Uterine fibroids, which are benign tumours that grow within the uterine wall, can cause severe pain and heavy bleeding, leading to this surgery. Similarly, endometriosis, a condition where uterine lining tissue grows outside the uterus, can cause chronic pain and fertility issues, often leading to the need for a hysterectomy.
Abnormal Bleeding and Severe Pelvic Pain
Hysterectomy is commonly recommended for individuals experiencing abnormal vaginal bleeding or severe pelvic pain that does not respond to other treatments. Abnormal bleeding may include heavy menstrual periods lasting more than seven days or bleeding between periods. Severe pelvic pain, often associated with conditions like adenomyosis—where the inner lining of the uterus breaks through the muscle wall—can also lead to considering a hysterectomy.
Preventive Measures for High-Risk Cancer Patients
For patients at high risk of certain types of cancer, particularly those with a strong family history or genetic predisposition, a hysterectomy may serve as a preventive measure. For example, individuals with BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations have a higher probability of developing ovarian and breast cancers. In such cases, removing the uterus, and often the ovaries and fallopian tubes, can significantly reduce the risk of cancer development.
As we move forward into the procedural aspects of hysterectomy, understanding the different approaches and preparations necessary will further clarify its comprehensive management and impact on health.
Types of Hysterectomy
A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the uterus, and there are several types tailored to address specific medical conditions and patient needs. Understanding these types is crucial for making informed decisions regarding surgical options.
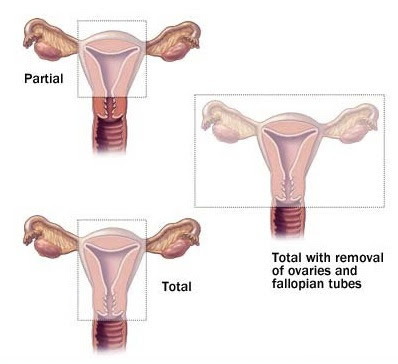
Total Hysterectomy: This is the most common form of hysterectomy, where the entire uterus, including the cervix, is removed. It is often recommended for conditions like uterine fibroids, heavy bleeding, or cancer. By removing both the uterus and cervix, the risk of cervical cancer is also mitigated.
Supracervical (Partial) Hysterectomy: In this procedure, only the upper part of the uterus is removed, leaving the cervix intact. This approach may be chosen when preserving pelvic floor support is desired, or to maintain a semblance of normalcy in sexual function, although these potential advantages should be weighed against the ongoing need for cervical cancer screening.
Total Hysterectomy with Bilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy: This surgery involves removing the uterus, cervix, both ovaries, and fallopian tubes. It’s typically performed for cancer treatment or if there is a risk of ovarian or other gynecological cancers. It’s important to note that this procedure induces menopause immediately if the patient hasn’t already undergone it, due to the removal of the ovaries, which produce key hormones.
Radical Hysterectomy: This extensive procedure is generally reserved for certain cancers, such as cervical cancer. It involves removing the uterus, cervix, the top portion of the vagina, and surrounding tissues, including possible removal of the pelvic lymph nodes. It’s more invasive due to the need for thorough cancer management, and has a longer recovery period and potential for significant impacts on sexual and urinary function.
Each type of hysterectomy comes with its own recovery trajectory, benefits, and risks. The choice of procedure should be tailored to the individual’s medical condition, future health considerations, and personal preferences, often requiring thorough discussion with a healthcare provider to ensure alignment with the patient’s health goals.
Types of Hysterectomy Procedures
Abdominal Hysterectomy
An abdominal hysterectomy is executed through an incision in the abdomen, either horizontally just above the pubic bone or vertically extending up to or beyond the belly button, based on the surgical requirement. This approach is typically reserved for larger uteri, extensive disease spread, or when cancer is a concern. The surgeon enhances visibility and control during the procedure, ensuring comprehensive removal of the uterus and any involved tissues.
This method does require a longer recovery period, often necessitating a hospital stay of two to three days. The recovery time extends from six to twelve weeks, primarily influenced by the incision size and the overall complexity of the surgery. Due to the invasiveness, patients might experience more post-operative pain and longer-lasting soreness compared to minimally invasive approaches.
Laparoscopic and Robotic Hysterectomy
Minimally invasive hysterectomy options, such as laparoscopic and robotic-assisted hysterectomy, utilise smaller abdominal incisions, generally resulting in shorter recovery times and less post-operative discomfort. In a laparoscopic hysterectomy, a video camera-equipped endoscope is inserted through an incision near the belly button. The abdomen is then distended with gas, creating a space for the surgeon to operate. Surgical tools are used through additional small incisions to detach and remove the uterus either in pieces or through a small incision.
A robotic-assisted hysterectomy operates on a similar principle but with the added precision and control of robotic instruments. The surgeon manoeuvres robotic arms from a console, translating their hand movements into smaller, more precise actions. Both these methods typically allow same-day discharge or a hospital stay of one night.
Vaginal Hysterectomy
A vaginal hysterectomy involves the removal of the uterus through an incision made at the top of the vagina. This method eliminates the need for abdominal incisions, leading to fewer complications and a generally faster recovery time. Surgeons use dissolvable stitches inside the vagina, and many patients can go home the same day. Recovery is often less painful and quicker, with most individuals returning to normal activities within four weeks.
Each hysterectomy approach presents its benefits and limitations. These include factors like the size and position of the uterus, underlying health conditions, and the surgeon’s expertise. Understanding the different types of hysterectomy procedures is vital as it helps align patient expectations and facilitates better decision-making regarding the most appropriate surgical option available.
By weighing the pros and cons of each method, patients and healthcare providers can collaboratively determine the best course of action tailored to the individual’s medical needs and recovery preferences.
Pre-Surgery Preparation
Required Diagnostic Tests and Health Evaluations
Before undergoing a hysterectomy, a series of diagnostic tests and health evaluations are essential to ensure the patient’s suitability for surgery. Typical evaluations include a complete blood count (CBC), blood chemistry tests, and urinalysis to check for any underlying health issues. An electrocardiogram (EKG) might also be necessary for patients with a history of heart disease. Imaging tests such as ultrasounds, MRI, or CT scans help assess the size and position of the uterus and detect any abnormalities in the pelvic region.
Discussion with Healthcare Provider
An in-depth discussion with the healthcare provider is crucial in preparing for a hysterectomy. Patients should understand the details of the procedure, the chosen surgical method, and any potential complications. Topics of discussion will include the patient’s medical history, the specific reason for the hysterectomy, and the expected outcomes. Patients are encouraged to voice their concerns and ask questions about the recovery process, any risks involved, and potential impacts on long-term health and lifestyle.
Planning for Post-Surgery Support and Recovery
Successful recovery from a hysterectomy relies heavily on effective post-operative care and support. Patients should plan for assistance during the initial days of recovery, considering factors such as mobility and daily tasks. Arranging for help with chores, childcare, and transportation ensures a smoother recovery process. The surgeon and healthcare team will provide specific post-operative care instructions, which may include restrictions on physical activity, signs of complications to watch for, and guidance on managing pain and other symptoms.
Understanding these aspects thoroughly helps patients be better prepared mentally and physically for the procedure, making the entire process less daunting and more manageable.
The Surgical Process
Anesthesia Options
Two primary anesthesia options are available for hysterectomy procedures: general anesthesia and regional anesthesia. General anesthesia involves administering medication that induces a state of unconsciousness, ensuring the patient remains asleep throughout the procedure. This approach is commonly preferred due to its ability to provide complete pain relief and comfort during surgery.
Regional anesthesia, also known as epidural or spinal anesthesia, involves injecting medication near the nerves in the lower back to block pain in the lower half of the body. Patients remain awake but numb from the waist down. While this method is less commonly used for hysterectomies, it may be an option for certain cases based on patient health and preferences.
Surgical Methods and Techniques
The choice of surgical method is influenced by factors such as the patient’s condition, the surgeon’s expertise, and the complexity of the procedure.
Abdominal Hysterectomy: This traditional method involves a horizontal or vertical incision in the abdomen, through which the uterus is removed. It is often utilised for larger uteri or when additional access to the pelvic organs is necessary.
Laparoscopic Hysterectomy: In this minimally invasive technique, small incisions are made in the abdomen to insert a laparoscope—a thin tube with a video camera—and surgical instruments. This method allows for a quicker recovery and less post-operative pain.
Robotic-Assisted Hysterectomy: Similar to laparoscopic hysterectomy, this technique employs robotic technology to enhance precision and control. Surgeons operate from a console while robotic arms perform the procedure through small incisions.
Vaginal Hysterectomy: The uterus is removed through an incision at the top of the vagina, eliminating visible scarring on the abdomen. This method generally results in fewer complications and a swift recovery.
Immediate Post-Operative Care
Following the hysterectomy procedure, immediate post-operative care is crucial to ensure a smooth recovery. Patients are taken to a recovery room where healthcare providers monitor vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels. Pain management is initiated, typically involving a combination of medications to alleviate discomfort.
Patients may experience vaginal bleeding and nausea, which are common and generally manageable. The healthcare team will provide guidance on positioning, breathing exercises, and early ambulation (walking) to prevent blood clots and enhance recovery.
As the recovery process begins, it is essential for patients to adhere to their healthcare provider’s recommendations and attend follow-up appointments for optimal healing and monitoring. This initial aftercare sets the foundation for a successful recuperation and the subsequent stages of long-term recovery.
Recovery and Aftercare
Expected Recovery Timeline
The recovery period following a hysterectomy typically spans from four to eight weeks, depending on the type of procedure performed. Recovery from a vaginal or laparoscopic hysterectomy often ranges from two to four weeks, while an abdominal hysterectomy generally requires a longer period, between six to eight weeks. It’s crucial to adhere to your healthcare provider’s guidelines and gradually increase your activity level during the recovery phase to avoid complications.
Post-Operative Care Instructions and Restrictions
Post-operative care is critical to ensuring a smooth recovery. Patients will receive detailed instructions from their healthcare provider, which may include:
Avoiding heavy lifting and strenuous activities for at least six weeks.
Consuming a balanced diet to promote healing and prevent constipation.
Engaging in light physical activities such as walking to improve circulation and prevent blood clots.
Managing pain with prescribed medications and following a regular pain management schedule.
You can expect light vaginal bleeding or dark brown discharge for up to six weeks post-surgery.. It’s recommended to use only light panty liners or sanitary pads during this period. Additionally, maintaining proper hygiene and monitoring the surgical site for signs of infection is vital.
Follow-Up Appointments and Monitoring
Follow-up appointments play a significant role in post-surgery recovery. Typically, your first follow-up visit will occur two weeks after the procedure. During these visits, your healthcare provider will:
Assess the healing process and address any concerns or complications.
Remove any stitches or staples, if applicable.
Adjust medications based on your recovery progress.
Provide further instructions on activity levels and restrictions.
Continued monitoring over the following months ensures that you are healing properly and helps address any potential issues that may arise. It’s important to communicate openly with your healthcare provider throughout this period.
Understanding the essential aspects of recovery and aftercare is vital for a successful recuperation process. Timely follow-up and adherence to post-operative instructions contribute significantly to your overall health and recovery journey.
Benefits and Long-term Effects
Relief from Chronic Conditions and Symptoms
One of the primary benefits of undergoing a hysterectomy is the relief from symptoms associated with chronic medical conditions such as fibroids, endometriosis, and uterine cancer. Individuals who experience persistent pelvic pain, heavy or irregular menstrual bleeding, and other debilitating symptoms often find significant improvement in their quality of life post-surgery. Removing the uterus effectively eliminates the root cause of these conditions, offering a sense of relief that can greatly enhance daily living and overall well-being.
Impact on Reproductive Health and Menstruation
A hysterectomy has a profound impact on reproductive health. Most notably, the procedure results in the cessation of menstruation, as the uterus is the organ responsible for the menstrual cycle. This means that individuals who undergo the surgery will no longer experience menstrual periods, which can be a significant relief for those who suffer from heavy or painful menstruation. However, it is crucial to consider that this also results in the permanent inability to conceive and bear children. Therefore, patients should thoroughly discuss reproductive plans and options with their healthcare provider prior to the procedure.
Quality of Life Improvements
Undergoing a hysterectomy can lead to substantial quality of life improvements. For many, the alleviation of chronic pain and bleeding translates into a more active and comfortable lifestyle. Individuals are often able to return to regular activities and hobbies that were previously hindered by their symptoms. Additionally, the removal of the uterus reduces the risk of uterine and cervical cancers, providing a sense of security and peace of mind for those with high cancer risk.
The psychological and emotional benefits of a hysterectomy should not be overlooked. While the decision to have the procedure can be emotionally taxing, many patients report feeling a renewed sense of well-being and freedom from the anxiety of ongoing medical issues. To support this transition, it is recommended to engage with counselling services or support groups to navigate the emotional adjustments following the surgery.
Understanding the positive outcomes of a hysterectomy is essential for those considering the procedure. However, it is equally important to acknowledge the potential risks and complications associated with surgery.
Risks and Complications
Potential Surgical Complications and Side Effects
Hysterectomy, while generally safe, carries potential surgical risks and side effects. Some of the most common risks include:
Excessive bleeding: Significant blood loss may occur during the surgery, necessitating a blood transfusion.
Post-operative infections: Infections at the surgical site or within the pelvis can develop post-operation.
Damage to nearby organs: The bladder, intestines, and blood vessels are at risk of damage during the surgery.
Adverse reactions to anesthesia: Reactions can range from mild to severe, including complications like respiratory issues.
Patients might also experience a variety of side effects:
Vaginal bleeding and discharge: This can persist for several weeks following a hysterectomy.
Soreness and irritation at incision sites: Expected around surgical areas, especially in abdominal hysterectomy.
Difficulty with urination or bowel movements: This is usually a result of temporary disruption caused by surgery.
Emotional and Psychological Considerations
A hysterectomy can have significant emotional and psychological impacts. Many patients report feelings of loss, especially concerning their reproductive capabilities. This procedure can bring about early menopause if the ovaries are removed, which also contributes to emotional distress and symptoms such as mood swings, hot flashes, and irritability. Psychological support and counselling are essential to help cope with these changes.
Possible Need for Hormone Replacement Therapy
If the ovaries are removed during the hysterectomy, patients are likely to enter menopause immediately. This sudden change may necessitate hormone replacement therapy (HRT) to manage symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and increased risk of osteoporosis and cardiovascular disease. HRT aims to replace hormones no longer produced by the ovaries, helping to alleviate these symptoms and improve quality of life.
The complexity and implications of hysterectomy necessitate thorough understanding and careful evaluation of benefits against potential risks. Proper post-surgical care and psychological support are pivotal for recovery and long-term well-being.
Cost Considerations
Price Range for Different Types of Procedures
Hysterectomy costs vary significantly based on the type of procedure performed. In regions like Hyderabad, India, costs range from Rs. 30,000 to Rs. 1,50,000.
Abdominal Hysterectomy: This traditional method is usually the most costly due to the hospital stay and recovery time required.
Laparoscopic and Robotic-Assisted Hysterectomy: These minimally invasive options generally incur higher equipment and expertise costs. However, shorter hospital stays and faster recoveries can offset some expenses.
Vaginal Hysterectomy: Often less expensive due to the absence of large incisions, reducing hospital stay and recovery time.
Factors Affecting Overall Cost
Several factors influence the overall cost of hysterectomy:
Hospital Type: Private hospitals typically charge more than public hospitals due to advanced facilities and services.
Surgeon’s Expertise: The experience and reputation of the surgeon can significantly impact the price.
Geographic Location: Costs fluctuate based on the city and country where the surgery is performed due to varying healthcare systems and living expenses.
Type of Procedure: As mentioned, different surgical methods entail different costs related to equipment, anaesthesia, and duration of hospitalisation.
Insurance Coverage and Payment Options
Health insurance plays a crucial role in managing the financial burden of a hysterectomy. Most insurance policies partially or fully cover the procedure if it is deemed medically necessary. However, patients should verify coverage details with their provider to avoid unexpected expenses.
Hospital Choice: Policies might have preferred hospitals where the insurance coverage is maximised.
Co-Payments and Deductibles: Patients are often required to pay a part of the total cost either as a co-payment or through deductibles.
Out-of-Pocket Costs: Non-covered services such as specific tests, consultations, or post-operative care may need to be paid out-of-pocket.
Planning and understanding these aspects ensure financial preparedness and prevent unforeseen expenses during and after the procedure.
In the subsequent sections, discussing financial management and exploring long-term benefits will provide a comprehensive view of the hysterectomy process.
Take the first step toward hassle-free hernia treatment today! At Magicward, we make it simple to compare surgery costs and find the best hospital tailored to your needs. Fill out the form now to receive personalized quotations from top hospitals in Hyderabad. Your health is our priority—let Magicward guide you to the right care at the right price!
Frequently Asked Questions about Hysterectomy
1. What is a hysterectomy?
A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the uterus. After the surgery, you will not menstruate or be able to get pregnant.
2. Why would a woman need a hysterectomy?
A hysterectomy may be necessary for treating cancer, abnormal uterine bleeding, uterine prolapse, fibroids, endometriosis, or chronic pelvic pain.
3. What are the types of hysterectomy?
The main types include total hysterectomy, supracervical (partial) hysterectomy, total hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, and radical hysterectomy.
4. What are the risks of a hysterectomy?
Risks include infection, bleeding, blood clots, injury to nearby organs, complications from anesthesia, and early menopause if ovaries are removed.
5. How long is the recovery period after a hysterectomy?
Recovery can take 4-6 weeks, but it varies based on the type of hysterectomy performed and the individual’s health condition.
6. Can you get pregnant after a hysterectomy?
No, pregnancy is not possible after a hysterectomy since the uterus is removed.
7. What are the common complications post-hysterectomy?
Complications may involve infections, blood clots, damage to the urinary tract or bowel, and vaginal cuff dehiscence.
8. What is the recovery process like after a hysterectomy?
Recovery usually involves hospital stay for 2-3 days, followed by several weeks of reduced activity. Patients should avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities during this period.
9. Can you experience menopause symptoms after a hysterectomy?
Yes, if the ovaries are removed, estrogen levels decline, leading to menopause symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, and mood swings.

