Currently Empty: $0.00

Hernia Surgery in Hyderabad: Types, Costs & Recovery Guide


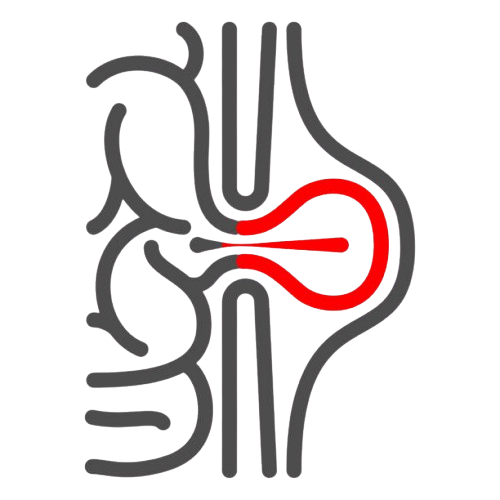
What is Hernia Surgery
Hernia surgery is a surgical procedure designed to repair hernias, which occur when an organ or tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the muscle walls. The primary goal of hernia surgery is to correct the bulging and reposition the displaced organs or tissues back to their proper place. This procedure is considered the most common and effective treatment method for hernias, with proven success in alleviating discomfort and preventing complications.
Types of Hernia
Inguinal Hernia
An inguinal hernia is the most common type of hernia and occurs when tissue, such as part of the intestine, protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles. This type typically affects the groin area and is more prevalent among men due to the natural weakness in the groin muscles. Symptoms can include a noticeable bulge, pain during activities like lifting, and discomfort when coughing or bending over.
Umbilical Hernia
An umbilical hernia happens when a part of the intestine bulges through the abdominal wall near the belly button. This hernia type is common in newborns but can also affect adults. In infants, umbilical hernias often close on their own by the age of 1 or 2. For adults, surgical intervention may be required if the hernia is large or causing discomfort.
Ventral Hernia
A ventral hernia occurs when tissue pushes through an opening in the muscles along the midsection of the abdomen. There are several subtypes, including epigastric hernias which appear between the navel and the lower part of the rib cage, and incisional hernias that arise at the site of a previous surgical incision. Ventral hernias can develop due to weaknesses in the abdominal wall caused by surgery, injury, or conditions like obesity.
Femoral Hernia
Femoral hernias are less common and mainly affect women. This type occurs when tissue bulges through the wall of the femoral canal, which carries blood vessels to the thigh. Due to the canal’s narrowness, femoral hernias have a higher risk of strangulation, which can cut off blood flow to the herniated tissue and require emergency surgery.
Hiatal Hernia
A hiatal hernia happens when the upper part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. Hiatal hernias are mostly asymptomatic, but larger ones can cause symptoms similar to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), such as heartburn, chest pain, and difficulty swallowing. Surgical repair is considered when symptoms are severe or complications like bleeding or strangulation arise.
Causes and Contributing Factors
Hernias can develop due to a combination of muscle weakness and strain. Factors that contribute to the formation of a hernia include:
- Genetic predisposition
- Chronic coughing or sneezing
- Heavy lifting without proper technique
- Obesity or rapid weight gain
- Surgery involving an incision near the potential site of hernia
Understanding the various types of hernias helps in recognising symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment to prevent complications. When symptoms interfere with daily life or pose health risks, surgical intervention is often advised to correct the issue and reinforce the weak muscle areas.
By appreciating the complexity and nuances of hernia types, individuals can make informed decisions about their health care options and anticipate steps necessary for their well-being.
Understanding Hernia Surgery
Hernias can cause significant discomfort and, if left untreated, may lead to severe complications. Hernia surgery, also known as herniorrhaphy, focuses on pushing the protruded organ back into place and strengthening the muscle wall with stitches or surgical mesh to prevent recurrence.
Hernia repair surgery is typically necessary because hernias usually worsen over time and may not resolve on their own. Therefore, surgical intervention remains the definitive solution to address this condition.
Types of Hernia Surgery
There are three primary types of hernia surgery:
Open Surgery: This traditional method involves making a single large incision over the hernia site. The surgeon then pushes the herniated tissue back into place and repairs the muscle wall with stitches or surgical mesh for reinforcement.
Laparoscopic Surgery: Known as minimally invasive surgery, this approach uses several small incisions instead of one large cut. A laparoscope, a thin tube with a camera, is inserted through one of the incisions to provide a view of the internal organs on a monitor. The surgeon uses specialized instruments inserted through the other incisions to repair the hernia.
Robotic Surgery: This advanced technique involves the use of robotic instruments controlled by the surgeon. It provides enhanced precision and control, allowing for meticulous repair of the hernia through small incisions.
Effectiveness of Hernia Surgery
Hernia surgery is highly effective in treating hernias and preventing their recurrence. Studies have shown that the success rate of hernia surgeries is high, significantly improving the quality of life for patients. However, it is essential to follow postoperative care instructions and lifestyle modifications to minimize the risk of hernia recurrence.
Conclusion
Hernia surgery plays a crucial role in managing hernias and alleviating related discomfort. Understanding the different types of hernia surgeries and their effectiveness can help patients make informed decisions about their treatment options.
Types of Hernia Surgery
Hernia surgery can be broadly classified into three types: open surgery, laparoscopic surgery, and robotic surgery. Each type offers unique advantages and is selected based on the specific patient condition, the type and size of the hernia, and the individual’s overall health.
Open Surgery
Open surgery is the traditional method typically used for larger hernias. In this approach, the surgeon makes a single large incision over the herniated area, allowing direct visualisation and access to the hernia. This type of surgery is often preferred for complicated or large hernias due to its comprehensive nature.
The procedure involves repositioning the herniated tissue back to its original place and reinforcing the weakened muscle wall. Surgeons often use surgical mesh to strengthen the repaired area, preventing recurrence of the hernia. Open surgery is usually performed under local anesthesia, though general anesthesia might be required depending on the case complexity.
Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery, often referred to as “minimally invasive” surgery, involves making several small incisions rather than a single large one. Through these small incisions, a laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera) is inserted into the abdomen, allowing the surgeon to view the hernia internally on a screen.
This technique is particularly beneficial due to less postoperative pain, minimal scarring, and a quicker recovery time compared to open surgery. It’s often chosen for smaller hernias or when cosmetic concerns are paramount. However, there can be a slightly higher risk of hernia recurrence with laparoscopic surgery ..
Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery is a variation of laparoscopic surgery that uses advanced robotic systems to assist in the hernia repair process. The surgeon operates at a console, controlling robotic arms that perform the procedure. This approach provides greater precision, flexibility, and control, allowing for more intricate movements that are impossible with human hands.
Robotic surgery combines the benefits of laparoscopic surgery, such as smaller incisions and faster recovery, with enhanced precision, potentially reducing the recurrence rates even further.
Each of these surgical types has its indications and is chosen based on a thorough evaluation of the patient’s specific conditions. As we have reviewed, choosing the right type of surgery depends largely on the individual’s circumstances and the healthcare provider’s recommendation.
Reasons for Hernia Surgery
Persistent Pain or Discomfort
Persistent pain or discomfort is a primary reason for seeking hernia surgery. Hernias often cause significant pain and distress, which can interfere with daily activities. Patients may experience pain when lifting objects, coughing, sneezing, or even standing up. This constant discomfort can reduce the quality of life, making it necessary to consider surgical intervention. By repairing the hernia, surgery aims to alleviate this pain, allowing individuals to return to their normal routines unimpeded.
Risk of Complications
Another critical reason for undergoing hernia surgery is the risk of complications if the condition is left untreated. One of the most serious complications is organ strangulation, where the protruding tissue becomes trapped and its blood supply is cut off. This can lead to tissue death and severe infections, making surgery an urgent necessity in such cases. Other potential complications include bowel obstruction and intestinal blockages, which also require surgical resolution to prevent life-threatening scenarios.
Prevention of Future Health Issues
Beyond addressing immediate symptoms and risks, hernia surgery is often recommended to prevent future health issues and the growth of the hernia. Untreated hernias tend to enlarge over time, increasing the risk of further complications and pain. By opting for surgery, patients can preemptively manage their condition, reducing the likelihood of reoccurrence and ensuring long-term relief. This proactive approach is particularly important for those with active lifestyles or jobs that involve physical strain, as it helps maintain their health and mitigate potential disruptions caused by hernia-related complications.
Hernia surgery is vital in managing the symptoms, mitigating risks, and preventing future growth of hernias. The next chapter will delve into the specifics of the surgical procedure itself.
The Surgical Procedure
Hernia surgery is a carefully orchestrated process beginning with anesthesia, proceeding to tissue repositioning and muscle wall repair, and sometimes incorporating surgical mesh for added reinforcement.
Administration of Anesthesia
The first step in hernia surgery is the administration of anesthesia, tailored to the type of surgery and the patient’s condition. For laparoscopic procedures, general anesthesia is typically used to put the patient into a deep sleep, ensuring no pain is felt. For open surgeries, local or regional anesthesia may suffice; this numbs the surgical area while the patient remains awake but feels no pain or discomfort in the operative site.
Repositioning of Herniated Tissue
After anesthesia takes effect, the surgeon proceeds to reposition the herniated tissue. In open surgery, this involves making a single, sizeable incision to access the affected area. In contrast, laparoscopic surgery uses multiple small incisions, allowing insertion of a laparoscope—a tiny camera that provides a magnified view of the internal structures on a video monitor . Robotic surgery is a variation of laparoscopic surgery, employing robotic instruments controlled by the surgeon for increased precision and a potentially better outcome.
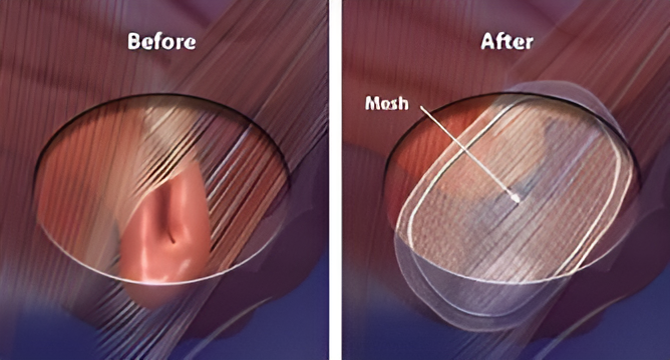
Repair of Muscle Wall and Reinforcement
The next crucial step involves repairing the weakened muscle wall. The surgeon sutures the muscle tissue to close the gap through which the hernia protruded. In many cases, especially those involving larger hernias or recurrent issues, inserting a surgical mesh to reinforce the muscle wall is recommended. This mesh acts as a supportive scaffold that strengthens the repaired area and reduces the risk of future hernias.
Closing the Incision
Finally, the incisions are closed with sutures or staples and then dressed to protect the wound from infection. The duration of the procedure varies significantly based on the complexity of the hernia and the chosen surgical method. While simple repairs may take as little as 30 minutes, more complex procedures can extend up to several hours.
As we conclude the description of the surgical procedure, it becomes clear why each step, from administration of anesthesia to muscle wall reinforcement, is pivotal in ensuring a successful outcome and minimising the risk of complications.
Recovery and Post-Surgery Care
Gradual Return to Normal Activities
Recovery from hernia surgery largely depends on the type of surgery performed and the individual patient’s overall health. Typically, patients are encouraged to gradually resume their normal activities post-surgery. For those who undergo open hernia surgery, the recovery period might be longer due to the larger incision involved. In contrast, laparoscopic and robotic surgeries often allow for a faster return to normal activities due to their minimally invasive nature.
Light Exercise
Light exercise, such as walking, is generally permitted soon after surgery. Walking helps to improve circulation, reduce the risk of blood clots, and promote healing. It is important to note that while light activity is encouraged, patients should avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting until their doctor advises that it is safe to do so. This gradual progression is crucial in ensuring a smooth recovery and preventing complications.
Return to Work
The timeline for returning to work varies significantly based on the type of hernia surgery, the patient’s overall health, and the nature of the job. For less physically demanding jobs, such as desk work, many patients may return to work within a few days to a week post-surgery. Jobs that require heavy lifting or strenuous activity may necessitate a longer leave, often several weeks, to ensure that the repaired area is fully healed and to prevent recurrence or injury. It is essential for patients to follow their surgeon’s specific recommendations regarding their return to work and activities.
Recovery from hernia surgery is a critical phase that requires careful adherence to medical advice and a paced return to normal activities. This approach aids in preventing complications and ensures a smoother transition back to daily life.
Risks and Complications
Short-term Risks
Hernia surgery, while generally safe and effective, carries several short-term risks that patients should be aware of.
Infection
Post-operative infection is a common risk associated with hernia surgery. It occurs when bacteria infiltrate the surgical site, causing symptoms such as redness, swelling, pain, and fever. Proper wound care and hygiene protocols can help mitigate this risk.
Seromas and Hematomas
Seromas are pockets of clear fluid that sometimes accumulate near the surgical site. Hematomas, on the other hand, are collections of blood outside of blood vessels. Both conditions can cause swelling and discomfort and may require drainage if they do not resolve on their own.
Bleeding and Bruising
Bleeding can occur during or after surgery, leading to significant bruising around the incision site. This is typically monitored and controlled by the surgical team but can occasionally require additional intervention.
Long-term Complications
Long-term complications, although less common, can have a significant impact on the patient’s recovery and overall health.
Mesh-related Issues
When surgical mesh is used to reinforce the muscle wall, there can be complications such as mesh migration and erosion. Mesh migration occurs when the mesh moves from its original placement, potentially leading to chronic pain and the need for additional surgeries. Mesh erosion happens when the mesh wears away or cuts into the surrounding tissues, causing discomfort and other complications.
Hernia Recurrence
Despite the effectiveness of hernia surgery, there is always a possibility of recurrence. Hernia recurrence rates are generally low, but they vary depending on factors such as the type of hernia, the surgical method used, and the patient’s adherence to post-surgery care instructions.
To minimise these risks and complications, it is important to follow your surgeon’s advice regarding pre- and post-operative care. This includes attending all follow-up appointments, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and promptly reporting any unusual symptoms or concerns.
By understanding these potential risks and taking proactive steps, patients can significantly improve their chances of a smooth recovery and long-term success post-hernia surgery.
Cost Considerations
When contemplating hernia surgery, understanding the associated costs is crucial for patients in order to make well-informed decisions regarding their treatment plan. In Hyderabad, the cost for hernia surgeries varies significantly based on the type of procedure undertaken, the complexity of the hernia, and the specific facilities of the chosen hospital.
General Hernia Surgery Costs
For traditional open hernia surgeries, the costs typically range from Rs27,000 to Rs45,000. This method, which involves a single large incision, is more suitable for extensive repairs and is relatively more affordable in comparison to other techniques. However, the overall expense can be influenced by factors such as the hospital’s location, its infrastructure, and the specific care provided.
Laparoscopic Surgery Costs
Laparoscopic hernia surgery, a minimally invasive option, is generally more expensive, with costs ranging between Rs80,000 to Rs1,20,000. This advanced procedure involves several small incisions and the use of a laparoscope for precise navigation and repair. The higher costs are attributable to the sophisticated equipment used and the specialised expertise required to perform the surgery.
Influencing Factors
Several factors contribute to the variation in the cost of hernia surgeries:
- Hospital Choice: Prestigious hospitals with advanced medical technologies and state-of-the-art facilities generally charge more. Hospitals in Hyderabad provide comprehensive care, contributing to the higher costs but ensuring quality treatment.
- Type and Complexity of Hernia: Different types of hernias such as inguinal, umbilical, femoral, and hiatal can cause fluctuations in the overall cost based on the required surgical approach and the complexity of the repair.
- Additional Interventions: Costs could rise if additional treatments are necessary, such as mesh reinforcement for the weakened muscle wall or extended postoperative care for complications like infections or seromas.
Understanding these cost variations helps in preparing financially for the procedure while ensuring access to the best possible care. This awareness also underscores the importance of choosing a reputable healthcare provider to minimise the risk of complications and ensure a successful recovery.
For further details and guidance, consulting with healthcare professionals and obtaining a personalised estimate based on a thorough examination of the hernia’s specifics is recommended.
Take the first step toward hassle-free hernia treatment today! At Magicward, we make it simple to compare surgery costs and find the best hospital tailored to your needs. Fill out the form now to receive personalized quotations from top hospitals in Hyderabad. Your health is our priority—let Magicward guide you to the right care at the right price!

