Currently Empty: $0.00

Open Heart Surgery in Hyderabad: Trusted Care for Your Heart
Understanding Open Heart Surgery
Open heart surgery is a medical procedure where surgeons gain direct access to the heart by opening the chest wall. This approach allows for the correction of various heart conditions that might be challenging to address using less invasive techniques. Open heart surgery’s primary purpose is to treat a range of cardiac issues, thereby improving a patient’s health and quality of life.



Definition and Purpose of Open Heart Surgery
The term “open heart surgery” fundamentally refers to any procedure where the chest is opened and surgery is performed on the muscles, arteries, or valves of the heart. The surgeon cuts through the breastbone, or sternum, and spreads the ribs to access the heart directly. This allows the surgeon to treat conditions that require precise and significant intervention. These surgeries can address issues such as blockages in the coronary arteries, damaged heart valves, or defects present from birth.
Major Types of Procedures
There are several major types of procedures that fall under the umbrella of open heart surgery.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): This is one of the most common forms of open heart surgery, used primarily to treat coronary artery disease. CABG involves creating a bypass around blocked arteries to restore sufficient blood flow to the heart muscle.
Valve Repairs and Replacements: Surgeons may repair or replace defective heart valves that are leaking or narrowed, improving the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively.
Heart Transplants: For patients with end-stage heart failure or severe heart diseases, a heart transplant may be necessary. This involves replacing the diseased heart with a healthy donor heart.
Repair of Congenital Heart Defects: Some people are born with heart defects that require correction through open-heart surgery, such as atrial septal defects (holes in the heart) or hypoplastic left heart syndrome (underdeveloped heart structures).
When Open Heart Surgery Becomes Necessary
Open heart surgery becomes indispensable when other treatments, such as medication or less invasive procedures, prove ineffectual. Conditions that often necessitate open heart surgery include:
Severe Coronary Artery Disease: When arteries supplying blood to the heart become blocked or narrowed, significantly restricting blood flow.
Heart Valve Disease: When valves are damaged or faulty, leading to improper blood flow through the heart.
Congenital Heart Defects: Structural issues present from birth that impair normal heart function.
Aneurysms and Cardiac Tumors: Enlarged sections of the heart or the presence of tumours that necessitate surgical intervention to prevent more severe complications
Open heart surgery is a critical and often life-saving procedure. The need for this surgery is determined by a combination of medical evaluations, diagnostic tests, and the failure of less invasive treatments.
Next, we will explore the various diagnostic tests required before undergoing open heart surgery to ensure patients are well-prepared for this significant procedure.
Pre-Surgery Diagnostic Tests
Before embarking on the journey of open-heart surgery, a series of diagnostic tests are pivotal. These tests not only assess the heart’s function but also the overall health of the patient. They ensure that the surgical procedure is tailored to the patient’s specific needs, leading to better outcomes.
Essential Tests
A few critical diagnostic tests are often conducted. The chest X-ray is a fundamental tool that provides a detailed image of the heart, lungs, and chest bones. This helps surgeons understand the heart’s size and the condition of the surrounding tissues.
Next, the electrocardiogram (EKG) is imperative. By recording the electrical activity of the heart, it can identify heart rhythm problems, previous heart attacks, and other abnormalities. Complementary to the EKG, an echocardiogram utilizes ultrasound waves to create a moving picture of the heart, showcasing the heart’s chambers, valves, and the surrounding structures in more detail.
Preoperative Medical Evaluations
Once these non-invasive diagnostic tests are complete, a comprehensive preoperative medical evaluation becomes necessary. This evaluation typically includes a detailed medical history review, a physical examination, and consultations with other medical professionals, such as anaesthesiologists and cardiologists. The goal is to identify any underlying health issues that could complicate surgery or recovery.
Cardiac catheterization might be performed, especially if coronary artery disease is suspected. This procedure involves inserting a catheter into a blood vessel to examine the coronary arteries’ condition. Stress tests, which involve exercising on a treadmill or taking medication that simulates physical activity, can further gauge the heart’s function under stress.
Importance of Comprehensive Health Assessment
A thorough health assessment goes beyond merely understanding the heart’s condition. It evaluates the patient’s overall well-being, determining their readiness for surgery and identifying potential risks. Conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and respiratory issues are taken into account. Additionally, lifestyle factors such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and diet are considered, as they could affect surgery outcomes and recovery.
Accurate diagnosis and health assessments lay the groundwork for successful open-heart surgery. Patients and healthcare providers can navigate the complexities of the procedure with greater confidence and clarity, leading to better health outcomes and efficient recovery processes.
With the essential diagnostic tests and evaluations providing a clear picture of the patient’s health, the focus shifts to understanding and addressing the financial aspects and cost factors associated with open-heart surgery in Hyderabad.
Cost Factors in Hyderabad
Average Cost Range
The cost of open heart surgery in Hyderabad ranges between 1.5 lakhs to 5 lakhs. This variation depends on multiple factors such as hospital facilities, the complexity of the procedure, and the patient’s health condition. Understanding these elements can help in planning and budgeting for the surgery effectively.
Factors Affecting Surgery Costs
Several crucial factors impact the overall cost of open heart surgery:
Type of Surgery
The specific type of surgical procedure required significantly influences the cost. For instance, a coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) may generally be less expensive than a heart transplant due to differences in complexity and resource needs. Understanding the type of surgery required allows for more accurate cost estimation.
Hospital Choice
The choice of hospital plays a vital role in determining the surgery cost. Private hospitals generally charge more for their advanced facilities and high-quality care, while government or charitable hospitals offer more budget-friendly options. It’s important to research and compare various hospitals to find one that fits your financial capacity and medical needs.
Location
The geographical location of the hospital can also impact costs. For example, open heart surgery in Hyderabad may be more affordable compared to other metropolitan areas in India due to differences in living expenses and medical infrastructure.
Patient’s Health Condition
A patient’s overall health and pre-existing medical issues can affect the cost. More complex health needs may necessitate additional tests, medications, and extended post-operative care, all of which can raise the overall expense. Comprehensive preoperative evaluations help in better understanding and planning for these additional costs.
Insurance Coverage and Payment Options
Insurance Plans
The extent of insurance coverage is a critical factor in managing the financial burden of open heart surgery. Comprehensive health insurance plans can significantly reduce out-of-pocket expenses. It is advisable to review your insurance policy to understand the coverage limits and exclusions.
Government Schemes
Exploring government-sponsored healthcare schemes can provide financial relief. These schemes offer assistance or coverage for heart surgeries to eligible patients, thereby reducing the financial strain. Verify eligibility and procedural requirements to benefit from these schemes.
Payment Options
For those without insurance, hospitals may offer various payment plans to make the cost more manageable. It’s also possible to negotiate discounts, especially if there are referrals from other healthcare providers or unique financial circumstances.
Understanding these cost factors and exploring various options can make the financial planning for open heart surgery more manageable, allowing patients to focus on recovery and well-being. Additionally, careful consideration of these elements can contribute to a more informed decision-making process when undergoing this significant medical procedure.
Next, we will delve into the significant benefits of undergoing open heart surgery, emphasizing health improvements and long-term outcomes.
Benefits of Open Heart Surgery
Improved Heart Function
Open heart surgery often results in significant improvements in heart function. Procedures such as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or valve repair/replacement can help restore adequate blood flow or ensure proper valve function, respectively. This restoration can alleviate symptoms like shortness of breath, chest pain, and fatigue, enabling patients to perform day-to-day activities more comfortably.
Enhanced Quality of Life
One of the most significant benefits of open heart surgery is the enhancement of overall quality of life. Patients typically experience a substantial reduction in symptoms post-surgery. This relief allows them to engage in physical activities and social interactions that were previously limited by their condition. The improved quality of life not only affects physical health but also boosts mental and emotional well-being, contributing to a more fulfilling life.
Longevity and Life-Saving Potential
For many patients, open heart surgery is life-saving. Conditions such as severe coronary artery disease or critical valve defects, if left untreated, can result in life-threatening situations like heart attacks or heart failure. By undergoing surgery, patients can significantly reduce the risk of such adverse events, thereby increasing their lifespan.
Reduction of Future Medical Interventions
Another significant advantage of open heart surgery is the potential reduction in the need for future medical interventions. Successfully addressing the core issue through surgery often diminishes the necessity for ongoing treatments, medications, or further surgeries. This not only reduces long-term medical costs but also minimizes the physical and emotional burden on patients.
Impact on Related Health Conditions
Open heart surgery can also positively affect other health conditions exacerbated by poor heart function. Improved blood circulation and heart efficiency can lead to better management of conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Patients often notice an overall improvement in their health status, which can make managing these co-existing conditions much easier.
Preparation for Surgery
Required Lifestyle Changes
Preparation for open heart surgery starts well before the day of the procedure. One of the most critical changes patients are advised to make is to quit smoking. Smoking cessation is essential because smoking hinders the body’s ability to heal and increases the risk of complications post-surgery. Alcohol consumption should also be limited or stopped entirely, as it can affect anesthesia and slow down the recovery process.
Medication Adjustments
Patients must discuss their current medications with their healthcare provider. Certain medications, particularly blood thinners such as aspirin or warfarin, need to be adjusted or discontinued a week or two before the surgery to reduce the risk of excessive bleeding during the procedure. Your healthcare team will provide specific instructions related to these medications and may prescribe alternatives to manage your condition without affecting the upcoming surgery.
Dietary Restrictions
Adhering to dietary restrictions is another critical preparation step. Patients are usually advised to fast, refraining from any food or drink for at least eight hours before surgery. An empty stomach helps reduce the risk of complications from anesthesia, making the procedure safer. Maintaining a healthy diet leading up to the surgery can also improve overall health, impacting recovery favourably.
Pre-Surgery Preparations and Documentation
Several logistical steps should be taken in preparation for surgery. This includes:
Medical Records: Ensure all medical records, including recent diagnostic tests, are up-to-date and available for the surgical team.
Legal Documentation: Prepare necessary legal documents, such as advance directives or a living will, and ensure they are accessible to your healthcare team.
Hospital Arrangements: Confirm hospital admission details, including the check-in time and any pre-admission requirements.
Home Arrangements: Arrange for someone to help at home post-surgery, as initial recovery might limit your physical capabilities.
By following these guidelines and closely adhering to medical advice, you can set the stage for a smoother surgical procedure and recovery process.
The Surgical Procedure
Step-by-Step Explanation of the Surgery Process
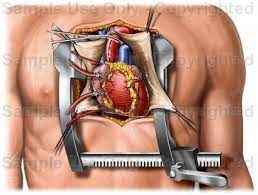
Open heart surgery begins with the patient being administered general anesthesia to ensure a pain-free experience. Once the patient is asleep, the surgeon makes a 6-8 inch incision down the middle of the chest. The breastbone is then cut and the ribs are spread apart to provide direct access to the heart.
The heart-lung bypass machine, critical for the procedure, is next connected to the heart. This machine takes over the function of both the heart and lungs, providing oxygenated blood to the rest of the body while the heart is stopped. Medication is administered to halt the heart’s beating, allowing the surgeon to perform the necessary repairs.
Duration and Anesthesia Requirements
The total duration of open heart surgery can vary greatly, typically ranging from 3 to 6 hours, depending on the complexity of the procedure. During this time, the patient is under general anesthesia, ensuring they remain unconscious. An anesthesiologist monitors the patient’s vital functions continuously throughout the surgery to address any complications that may arise.
Role of Heart-Lung Bypass Machine
The heart is connected to a heart-lung bypass machine which plays a vital role in maintaining circulation and oxygenation. The machine diverts blood from the heart, oxygenates it, and pumps it back into the patient’s body. This allows the surgeon to operate on a still heart, enhancing precision during delicate procedures such as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), valve repair, or heart transplant.
After the necessary heart repairs are completed, the heart-lung bypass machine is gradually disconnected. The heart is typically restarted using a mild electric shock or it may resume beating on its own. The surgeon then proceeds to close the breastbone with wires or sutures that stay inside the body, followed by closing the skin incision with stitches.
This intricate process transitions into the critical phases of recovery and rehabilitation, ensuring the patient’s return to a healthy and active lifestyle.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Initial Recovery in ICU and Hospital Stay Duration
Following open heart surgery, the patient’s initial recovery phase begins in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU). This phase is critical as it allows for close monitoring of vital signs, heart function, and the patient’s overall condition. Typically, a patient will stay in the ICU for one to two days. During this time, medical staff will ensure that the heart is functioning properly post-operation and that there are no immediate complications such as excessive bleeding or infection.
After the ICU, the patient is usually moved to a regular hospital room for an additional five to seven days. The duration of this stay may vary based on the patient’s response to the surgery and any underlying health conditions. The focus during this period is on stabilising the patient’s condition, managing pain, and preventing complications. Nurses and doctors will continuously monitor the patient’s progress, provide necessary medications, and begin initial rehabilitation steps.
Post-Operative Care and Pain Management
Effective post-operative care is essential for a smooth recovery. Pain management is a critical component, as managing pain allows patients to participate in necessary activities, such as breathing exercises and physical therapy. Physicians typically prescribe pain relievers, and the dosage is carefully monitored and adjusted based on the patient’s needs.
Other aspects of post-operative care include:
Wound Care: Ensuring the surgical incisions are clean and healing properly.
Respiratory Health: Encouraging deep breathing exercises to prevent lung infections and improve lung function.
Physical Activity: Gradual introduction of physical activities to promote circulation and prevent blood clots.
Nutritional Support: Providing a balanced diet that supports healing and recovery.
Long-Term Recovery Timeline (6-12 Weeks)
The complete recovery from open heart surgery generally spans six to twelve weeks. During this period, the patient will progressively resume normal activities under medical guidance.
Weeks 1-4
Follow-Up Visits: Regular check-ups to monitor heart function and overall health.
Gradual Physical Activity: Light exercises such as walking, gradually increasing intensity based on tolerance.
Medication Adjustments: Continuation and possible adjustment of prescribed medications.
Weeks 5-8
Enhanced Rehabilitation: Participation in structured cardiac rehabilitation programs aimed at improving cardiovascular health.
Lifestyle Modifications: Implementation of lifestyle changes such as a heart-healthy diet and smoking cessation.
Weeks 9-12
Increasing Physical Activities: Transition to more strenuous activities as deemed safe by the healthcare provider.
Continuous Monitoring: Regular health assessments to ensure no long-term complications such as arrhythmias or heart failure.
By the end of the twelve-week period, most patients can return to their daily routines, although complete healing and adjustment may take longer for some. Adherence to recommended follow-ups and lifestyle changes can significantly impact the long-term success of the surgery, promoting overall well-being and prevention of future heart issues.
This cohesive recovery plan aims to ensure a return to a healthy, active lifestyle while minimising the risk of post-surgical complications.
Risks and Complications
Open heart surgery, while often life-saving, comes with inherent risks and potential complications that one must consider seriously. The complications can range from immediate post-operative issues to long-term health concerns.
Common Post-Surgical Complications
Post-surgery, patients may encounter several complications which include, but are not limited to:
Allergic Reaction to Anesthesia: A significant risk during the surgery can be an adverse reaction to anesthesia, leading to severe complications.
Arrhythmias (Irregular Heartbeat): After surgery, the heart may experience abnormal rhythms, necessitating further intervention.
Bleeding: Excessive bleeding during or post-surgery is a common risk that might require additional surgical procedures to control.
Infections: The incision site is susceptible to infections which can sometimes become severe, requiring prolonged antibiotic treatment.
Blood Clots: Formation of clots post-surgery can travel to other parts of the body causing serious issues like pulmonary embolism or stroke.
Damage to Organs: Organs such as lungs or kidneys can be inadvertently damaged during the procedure.
Prevention and Management Strategies
Managing these complications involves a multi-faceted approach. Preventive strategies include:
Pre-surgical Assessments: Comprehensive evaluations to identify high-risk patients and tailor the surgical plan accordingly.
Sterile Techniques: Adherence to strict sterile protocols during surgery to minimise infection risks.
Anticoagulation Therapy: Carefully monitored anticoagulation therapy to prevent clot formation post-surgery.
Monitoring and Early Intervention: Continuous monitoring during the recovery phase allows for early detection and intervention of any complications.
Maintaining open communication between healthcare providers and the patient about any new or worsening symptoms is crucial for effective management.
Long-Term Health Considerations
Post open-heart surgery, patients must be vigilant about long-term health considerations to maintain their recovery and overall health:
Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation, is essential.
Medication Adherence: Strict adherence to prescribed medications, such as blood thinners or beta-blockers, to manage heart health.
Regular Follow-Ups: Ongoing check-ups with a cardiologist to monitor heart function and detect any late-emerging issues early.
Patients are encouraged to engage actively in their recovery process, which significantly improves outcomes and quality of life. Effective rehabilitation and lifestyle modifications can lead to a successful long-term recovery.
As patients transition from surgery to recovery, the focus shifts towards ensuring an effective recuperation process through rigorous follow-ups and supportive care.
Frequently Asked Questions about Open Heart Surgery
What is open heart surgery?
Open heart surgery is a procedure in which the chest is opened, and surgery is performed on the heart muscles, valves, arteries, or other structures within the heart.
Why is open heart surgery performed?
It is performed to treat serious heart conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart valve disease, heart defects, and aneurysms.
What are the risks associated with open heart surgery?
Risks include infection, bleeding, blood clots, stroke, heart attack, and complications from anesthesia.
How long does open heart surgery take?
The duration varies, but it generally takes between three to six hours.
What is the recovery time after open heart surgery?
Recovery time typically ranges from six to twelve weeks, depending on the individual’s health and the complexity of the surgery.
How should I prepare for open heart surgery?
Preparation may include undergoing various tests, stopping certain medications, fasting, and arranging for post-surgery care.
What type of anesthesia is used during open heart surgery?
General anesthesia is used, ensuring the patient is asleep and pain-free throughout the procedure.
What lifestyle changes are recommended after open heart surgery?
Post-surgery, patients are often advised to maintain a healthy diet, engage in regular exercise, avoid smoking, and follow a cardiac rehabilitation program.
Can open heart surgery be performed on children?
Yes, open heart surgery can be performed on children to correct congenital heart defects or other heart-related conditions.
What should I expect during the hospital stay for open heart surgery?
Patients usually stay in the hospital for about a week, with the first few days spent in the intensive care unit (ICU) for close monitoring.
Take the first step toward hassle-free hernia treatment today! At Magicward, we make it simple to compare surgery costs and find the best hospital tailored to your needs. Fill out the form now to receive personalized quotations from top hospitals in Hyderabad. Your health is our priority—let Magicward guide you to the right care at the right price!

