Currently Empty: $0.00

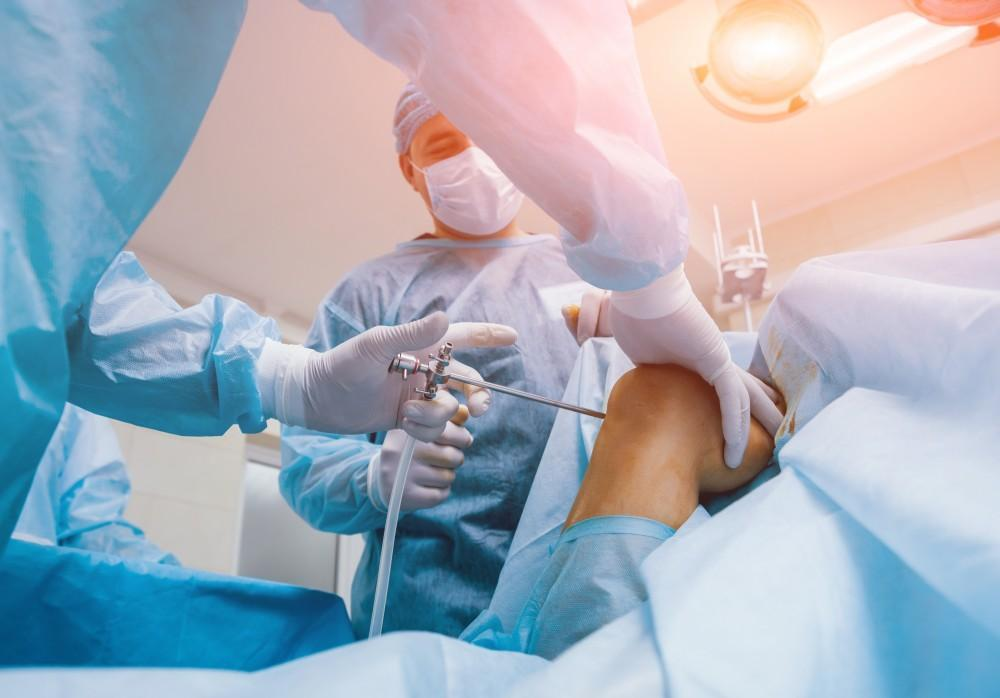
Knee Arthroscopy in Hyderabad: Expert Care for Pain-Free Movement
What is Knee Arthroscopy?
Minimally Invasive Surgical Procedure Using Small Incisions
Knee arthroscopy is a surgical technique that employs minimally invasive methods to address knee joint issues. This procedure involves making small incisions, typically about the size of a keyhole, through which the surgeon inserts specialised instruments. These tiny openings significantly reduce the trauma to surrounding tissues compared to traditional open knee surgery.



Uses a Tiny Camera (Arthroscope) and Specialised Tools for Diagnosis and Treatment
The cornerstone of knee arthroscopy is the arthroscope, a small camera inserted into the knee joint through one of the incisions. This camera transmits real-time images to a monitor in the operating room, allowing the surgeon to have a magnified view of the joint’s internal structures. This visual capability facilitates accurate diagnosis and enables the surgeon to repair or remove damaged tissues with precision.
Less Invasive Alternative to Traditional Open Knee Surgery
One of the most notable advantages of knee arthroscopy over open knee surgery is its minimally invasive nature. This approach results in less tissue damage, reduced post-operative pain, and a faster recovery time. Reduced incision size also minimises the risk of infection and scarring, making knee arthroscopy a safer and more cosmetically appealing option for patients needing knee surgery.
By offering detailed visualisation and treatment capabilities through small incisions, knee arthroscopy has become a preferred method for addressing various knee conditions. Transitioning from traditional surgery, this technique benefits both patients and surgeons, offering efficiency and efficacy in treatment without the extensive downtime associated with more invasive procedures.
As we continue, we will delve into the common reasons that drive the need for knee arthroscopy, helping to understand the diverse applications of this advanced surgical method.
Common Reasons for Knee Arthroscopy
Soft Tissue Injuries
One of the primary indications for knee arthroscopy is the presence of soft tissue injuries. This includes damage to ligaments, tendons, and the meniscus. These structures are essential for knee stability and function. For example, a torn ligament like the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) can severely disrupt knee mechanics, leading to instability and pain. Similarly, meniscus tears, common in athletes, can inhibit smooth joint movement and cause persistent discomfort. Using an arthroscope, surgeons can visualize the extent of the injury and perform necessary repairs, such as stitching torn tissues or trimming damaged parts to restore normal knee function.
Persistent Knee Pain
Another common reason for knee arthroscopy is to address persistent knee pain that has not responded to non-surgical treatments. Patients often try methods like physical therapy, medications, and corticosteroid injections without finding relief. Chronic pain might be due to conditions that are not easily identifiable through non-invasive imaging techniques. Arthroscopy allows for direct visualisation of the joint’s interior, providing a clear diagnosis and immediate intervention. This approach ensures that the underlying cause of the pain, whether it’s due to loose bodies or subtle cartilage damage, is effectively managed.
Diagnosing and Treating Knee Inflammation and Cartilage Damage
Knee arthroscopy is also valuable for diagnosing and treating inflammation and cartilage issues within the knee joint. Conditions like synovitis—where the lining of the joint becomes inflamed—can be challenging to pinpoint with conventional imaging. Arthroscopy enables surgeons to identify inflamed areas and remove the affected tissue, thereby reducing pain and swelling. Cartilage damage is another problem often treated with this method. Cartilage, which cushions the knee joint, can deteriorate due to acute injury or degenerative conditions. Arthroscopy allows surgeons to remove or repair damaged cartilage, improving joint function and reducing symptoms.
These reasons illustrate the versatility and effectiveness of knee arthroscopy in managing various knee problems. This minimally invasive procedure not only aids in accurate diagnosis but also provides a means for immediate treatment, promoting quicker recovery and improved outcomes for patients.
This discussion sets the stage for understanding how patients prepare for surgery while highlighting the benefits of early intervention.
Pre-Surgery Preparation
Proper pre-surgery preparation is crucial to the success of knee arthroscopy. Knowing what to expect and following your healthcare provider’s recommendations can enhance your recovery process and reduce potential risks.
Discussion of Current Medications and Necessary Adjustments
A thorough review of your current medications is essential. Inform your surgeon about all the medicines you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, and prescribed medications. Some medications, such as blood thinners, may need to be adjusted or temporarily discontinued to minimize the risk of bleeding during and after the surgery. Always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions regarding medication adjustments to ensure a safe procedure.
Fasting Requirements Before Surgery
Fasting is typically required before undergoing knee arthroscopy. You will be asked to abstain from eating or drinking for a specific period before the surgery, often starting from midnight the night before. This measure is essential to reduce the risk of aspiration and other complications related to anesthesia. Your exact fasting requirements will be outlined by your medical team, so it is crucial to adhere to their guidelines closely.
Guidelines for Clothing and Jewelry Removal
On the day of the surgery, you should wear loose-fitting and comfortable clothing. This will make it easier to change into and out of surgical gowns and will not put pressure on your knee post-surgery. You should also remove all jewelry and piercings before arriving at the hospital or surgical center. This includes rings, necklaces, earrings, and watches. Removing jewelry is important to prevent potential interference with medical equipment and to reduce the risk of infection.
Completing these pre-surgery steps ensures that you are well-prepared for knee arthroscopy, paving the way for a smoother surgical experience and recovery. The next stage involves understanding the surgical procedure itself.
Surgical Procedure
During knee arthroscopy, the administration of anaesthesia is a crucial first step. Depending on the specific needs of the patient and the complexity of the procedure, the anaesthesia may be local, numbing only the knee area, or regional, numbing the body from the waist down. In some cases, a general anaesthetic may be administered, rendering the patient completely unconscious during the operation. The aim is to ensure that the patient remains pain-free and comfortable throughout the surgery.
Once anaesthesia takes effect, the surgical team will cleanse and prepare the knee area, securing it in a stabilising device to maintain proper positioning. This preparation is key to minimising movement and ensuring a precise procedure. The surgeon then makes one or more small incisions around the knee. Typically, these incisions are less than an inch long, making them significantly less invasive compared to the traditional open knee surgery.
Through these incisions, an arthroscope – a narrow tube equipped with a small camera – is inserted into the knee joint. The camera transmits live images to a monitor in the operating room, providing the surgeon with a clear, magnified view of the internal structures of the knee. This visualisation is essential for accurately diagnosing the condition and guiding the surgical instruments used for repair.
Specialised surgical tools are then introduced through the additional small incisions. These may include scissors, shavers, or lasers, depending on the nature of the repair needed. The surgeon performs tasks such as trimming damaged cartilage, repairing torn ligaments, and removing loose fragments of bone or cartilage. The precise use of these tools ensures minimal disruption to the surrounding tissues, significantly aiding in a quicker recovery period post-surgery.
The entire procedure usually lasts about one hour, although the duration can vary based on the complexity of the knee condition being treated. After the necessary repairs are made, the surgeon removes the arthroscope and tools, and the small incisions are closed with sutures or surgical tape. A bandage is then applied to protect the area .
Cost Considerations
The cost of knee arthroscopy can vary significantly in Hyderabad, typically ranging from INR 85,000 to INR 2,000,000. This broad spectrum of costs stems from several factors influencing the final price of the procedure.
Factors Affecting Cost
Type of Equipment Used: Advanced, state-of-the-art arthroscopic equipment tends to cost more than standard options. The use of high-definition cameras and specialised surgical tools can drive up the total expense.
Surgeon’s Fees: The experience and reputation of the orthopedic surgeon play a crucial role in determining the cost. Surgeons with a high level of expertise and a track record of successful surgeries may charge higher fees.
Hospital Charges: Different hospitals have varying rates for surgical procedures, which include costs for the operating room, medical supplies, and postoperative care.
Anesthesia Fees: Whether local, regional, or general anesthesia is used, the type and duration can affect the total cost.
Pre and Postoperative Care: Costs could also include pre-surgery consultations, diagnostic tests, and postoperative follow-up visits and physical therapy sessions.
Regional Pricing Comparison
While the cost in Hyderabad can range between INR 85,000 and INR 2,000,000, these prices tend to be consistent with other parts of India. For instance, the cost of a similar procedure in regions like Bengaluru, Mumbai, and Delhi also falls within a comparable range. Factors such as location and the hospital’s reputation can cause slight variances, but overall, the pricing remains in a similar bracket.
The price might seem high, but it is important to consider the value that comes with advanced equipment, experienced surgeons, and comprehensive care. Many health insurance plans offer coverage for knee arthroscopy, which can significantly offset out-of-pocket expenses. Patients are advised to discuss with their healthcare provider and insurance company to understand the financial implications fully.
Understanding the cost considerations is essential for making informed decisions about knee arthroscopy. This awareness helps patients prepare better financially and ensures transparency between the healthcare provider and the patient.
Post-Surgery Recovery
Initial Recovery Period with Limited Weight-Bearing
Following knee arthroscopy, the initial recovery phase typically involves restricted weight-bearing on the affected knee. Patients are often advised to use crutches or a walker to assist with movement and to avoid placing undue stress on the knee. This period, lasting a few days to a week, allows the surgical site to begin healing, minimising the risk of complications such as swelling or further injury.
Pain Management and Swelling Reduction Techniques
Effective pain management and swelling control are critical components of the post-operative care plan. Pain relief can be achieved through the administration of over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or prescribed medication, as recommended by healthcare providers. Additionally, measures such as applying ice packs and keeping the leg elevated are beneficial for reducing swelling and discomfort. Elevating the knee above heart level can significantly help in decreasing inflammation during the crucial early days following surgery.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation Program
A carefully structured physical therapy program is essential for a successful recovery post-knee arthroscopy. This rehabilitation typically starts with gentle exercises to restore mobility and gradually progresses to strengthening exercises. Physical therapists work closely with patients to tailor exercises that enhance the range of motion and build muscle strength around the knee joint. The ultimate goal is to restore the knee’s full function and ensure the resumption of daily activities within 6-8 weeks. Compliance with the physical therapy regimen is crucial for achieving optimal recovery outcomes and minimizing the risk of long-term issues.
Recovery is a stepwise process, beginning with protection and gentle mobilisation of the knee, followed by strength training and, finally, the integration of more dynamic activities as one’s condition improves. This phased approach reduces the likelihood of complications and ensures a more comprehensive healing process.
Ensuring a robust recovery protocol paves the way for a successful and lasting return to one’s daily routine. The subsequent focus will be on understanding potential risks and complications that might arise post-surgery and strategies for their management.
Risks and Complications
Potential for Bleeding and Infection
Though knee arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure, it carries certain risks, including bleeding and infection. Bleeding can occur during or after the surgery, necessitating close monitoring of the wound site. Infection, though less common, can lead to serious complications if not promptly addressed. Symptoms of infection include increasing redness, swelling, warmth, and fever. Patients should report these symptoms to their healthcare provider immediately to avert further complications.
Possibility of Blood Clots
Blood clots are another potential risk associated with knee arthroscopy. These can form in the deep veins of the legs, a condition known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT). DVT can be dangerous if a clot travels to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. Signs of DVT include swelling, pain, and tenderness in the leg. Preventative measures, such as wearing compression stockings and early mobilisation, are crucial for reducing this risk.
Knee Stiffness
Knee stiffness can result post-surgery, limiting the range of motion and subsequently affecting recovery. This stiffness is often due to scar tissue formation around the knee joint. Physical therapy plays a vital role in preventing and treating stiffness. A well-structured rehabilitation program, involving specific exercises to improve flexibility and strength, can significantly mitigate this issue.
Managing Post-Operative Complications
Effective management of post-operative complications is essential for a successful recovery. Adhering to the prescribed pain management plan is crucial for controlling discomfort and swelling. Patients are often advised to use ice packs and keep the operated leg elevated to reduce swelling. Physical therapy is indispensable for restoring knee function and preventing complications like stiffness and weakness. Clinicians usually design a customised rehabilitation program that includes exercises tailored to the patient’s specific needs and progress.
Regular follow-up appointments are necessary to monitor the healing process and address any emerging issues promptly. Communication with healthcare providers about any unusual symptoms or concerns is vital for early intervention and complication management.
Post-surgery risks and complications require vigilant care and proactive management to ensure a smooth recovery. With the appropriate interventions and consistent adherence to medical advice, the likelihood of severe complications can be significantly reduced.
Long-term Outlook
Timeline for Returning to Daily Activities
The timeline for returning to daily activities after knee arthroscopy varies depending on individual recovery rates and the complexity of the procedure. Typically, most patients can expect to resume light activities, including walking and driving, within one to three weeks. However, engaging in more demanding or strenuous activities may require waiting six to eight weeks post-surgery. It is crucial to follow the guidance of your healthcare provider to ensure a smooth recovery and avoid premature stress on the knee.
Potential Lifestyle Modifications
To support long-term knee health, some patients might need to make lifestyle adjustments. Engaging in high-impact activities such as running or jumping can exacerbate knee damage. Therefore, doctors often advise switching to low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling, which are gentler on the knee joint. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the stress placed on the knee, further preventing potential injury or complications. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to tailor these modifications based on individual needs and recovery progress.
Expected Outcomes and Success Rates
The success rate of knee arthroscopy is generally high, with many patients experiencing significant relief from symptoms and a return to normal activities. The procedure’s effectiveness depends considerably on the specific knee condition being treated and the patient’s adherence to post-operative care, including physical therapy and lifestyle modifications. Studies suggest that most individuals regain full use of their knees when they diligently follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations and a structured rehabilitation plan. However, it is important to note that outcomes can vary from person to person based on factors such as the nature of the knee problem and overall health condition.
As patients navigate their recovery journey, staying informed and adhering to prescribed care protocols can greatly enhance the prospects of a successful long-term outcome.
Take the first step toward hassle-free hernia treatment today! At Magicward, we make it simple to compare surgery costs and find the best hospital tailored to your needs. Fill out the form now to receive personalized quotations from top hospitals in Hyderabad. Your health is our priority—let Magicward guide you to the right care at the right price!

